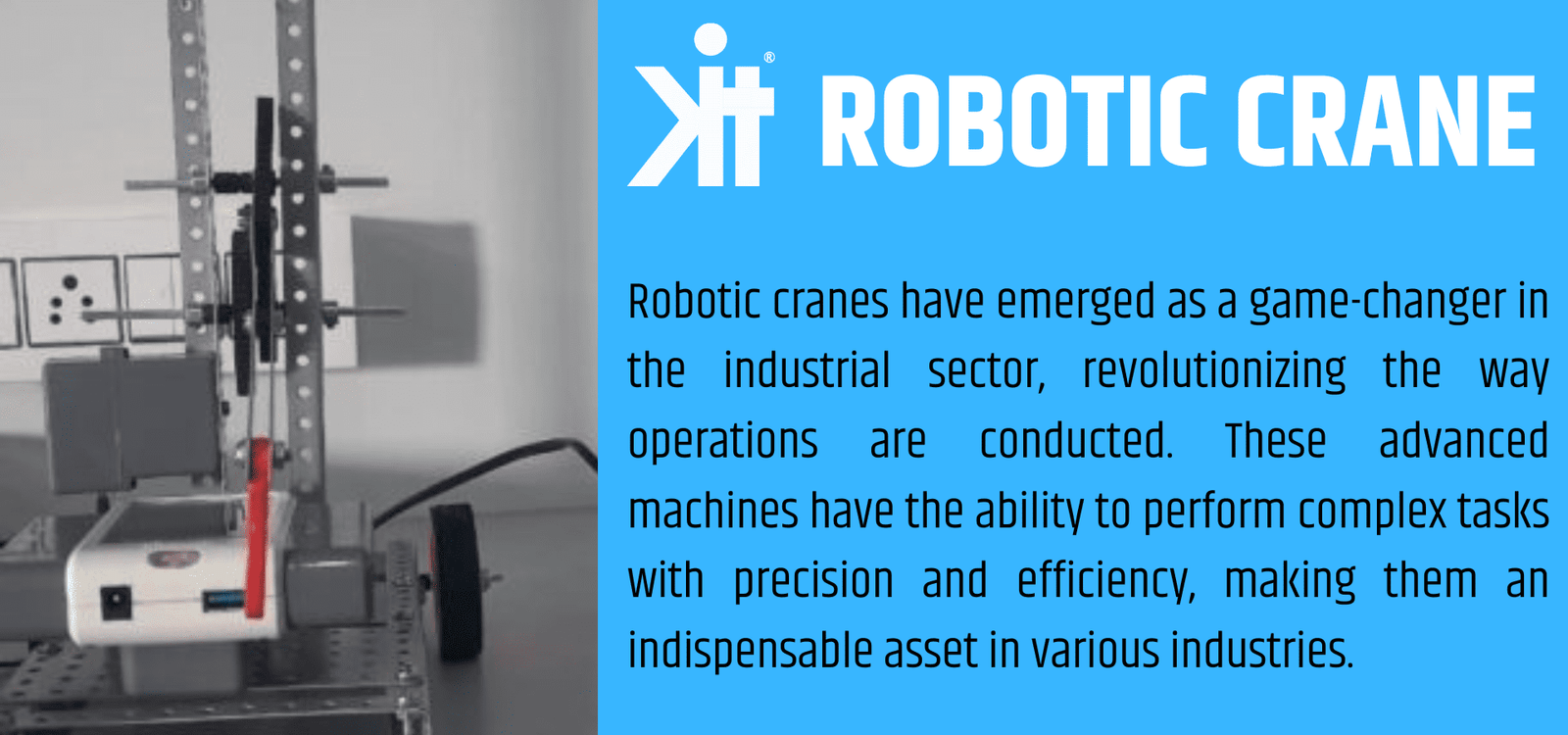
Robotic cranes have emerged as a game-changer in the industrial sector, revolutionizing the way operations are conducted. These advanced machines have the ability to perform complex tasks with precision and efficiency, making them an indispensable asset in various industries.
The process of robotic cranes involves several stages, each contributing to the overall efficiency and effectiveness of these machines. Let’s delve into the process and understand how these cranes work.
1. Design and Engineering
The first stage in the process of robotic cranes is the design and engineering phase. During this stage, experts analyze the specific requirements of the industry and develop a crane design that can meet those needs. Factors such as load capacity, reach, and maneuverability are considered to ensure optimal performance.
2. Manufacturing
Once the design is finalized, the manufacturing process begins. High-quality materials are used to construct the crane components, ensuring durability and longevity. Advanced manufacturing techniques are employed to maintain precision and accuracy during the assembly process.
3. Installation and Integration
After the manufacturing process, the robotic crane is installed and integrated into the existing infrastructure. This involves mounting the crane on a suitable structure and connecting it to the control system. The integration process ensures seamless communication between the crane and other machinery.
4. Programming and Calibration
Robotic cranes are programmed to perform specific tasks with utmost precision. During this stage, the crane’s control system is programmed to execute various operations such as lifting, moving, and placing objects. Calibration is also carried out to ensure accurate positioning and alignment.
5. Testing and Quality Assurance
Before the robotic crane is put into full operation, it undergoes rigorous testing and quality assurance procedures. This ensures that the crane functions flawlessly and meets all safety standards. Various tests are conducted to evaluate the crane’s performance under different conditions.
6. Operational Training
Once the robotic crane has passed all quality tests, operational training is provided to the operators. They are trained to operate the crane efficiently and safely. Proper training ensures that the crane is utilized to its full potential and minimizes the risk of accidents.
7. Deployment and Maintenance
Finally, the robotic crane is deployed for operational use. Regular maintenance and inspections are carried out to ensure optimal performance and prevent any potential breakdowns. Any necessary repairs or replacements are promptly addressed to minimize downtime.
Robotic cranes have revolutionized industrial operations by offering enhanced efficiency, precision, and safety. Their intricate process, from design to deployment, ensures that these machines are capable of meeting the specific requirements of various industries. With continuous advancements in technology, robotic cranes are expected to play an even bigger role in shaping the future of industrial operations.